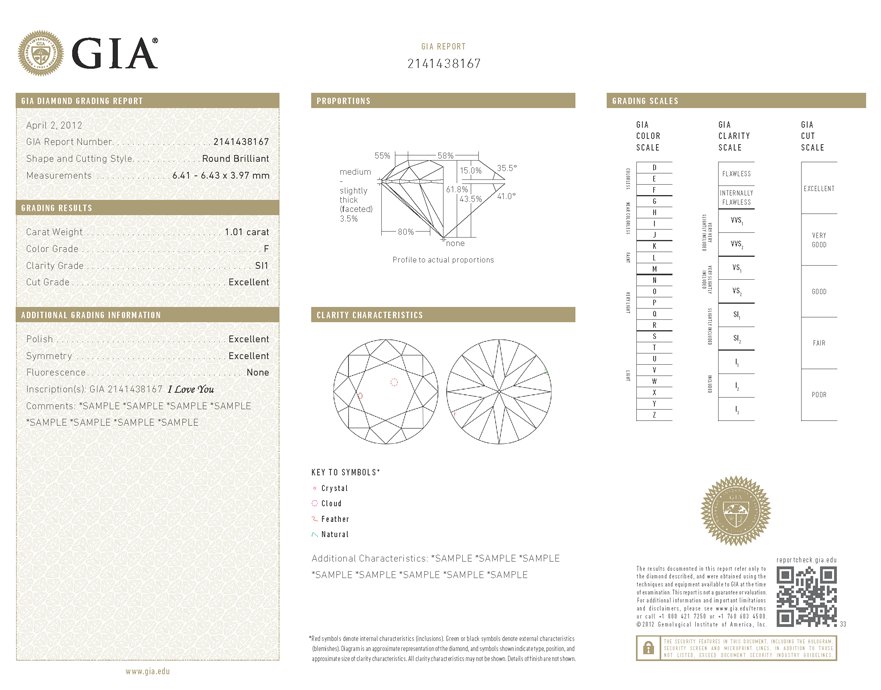
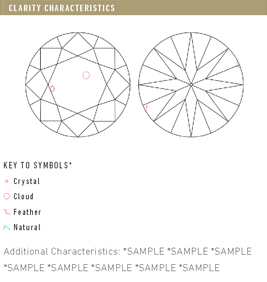
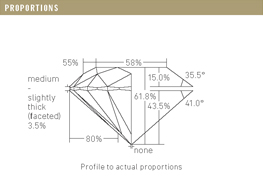
Definition
A Round Brilliant Cut is the modern era’s most popular selection for diamond jewelry. This perfected cut represents six generations of skilled cutters’ efforts to create the maximum light return in a diamond. A Brilliant Cut has a circular outline and a cone-like shape, with faceting patterns that create areas of light and dark contrast. Its triangular and quadrilateral facets are strategically placed to provide exceptional scintillation through the top facet of the gemstone, or its table. The faceting pattern of the modern Round Brilliant was developed in 1919 by Marcel Tolkowsky. Hailing from a family of diamond cutters, Marcel’s cut is based off mathematical calculations that took into account both the maximum brilliance and fire of a diamond. It is referenced to as a ‘Round Brilliant’ to distinguish it from earlier round shaped diamond cuts. The modern round cut consists or either 57 or 58 facets. There are 33 on its crown, or top, and 25 on its pavilion, or bottom. A round brilliant may or may not include a culet, or the bottom-most point facet. Tolkowsky found that if a diamond is cut too shallow or too deep light can escape out of the side or bottom of the gemstone, resulting in the loss of brilliance and fire.
Round Brilliant Facet Diagram
Considering a Round Brilliant Cut
Round Brilliant Cut diamonds are admired for their exceptional fire and modern aesthetic. Nearly 75% of diamonds sold in today’s marketplace are round shaped. The Gemological Institute of America, or GIA, introduced the 4Cs grading system to judge diamonds, with its cut grade exclusively created to evaluate Round Brilliant diamonds. A cut grade will determine how well a gemstone interacts with light. A well-cut diamond will reflect light within itself, from one mirror-like facet to another. If a diamond is dark it means it has been cut too deep or too shallow and light is being lost through the side or bottom. This reduces its brilliance and value, and for this reason we recommend a cut grade of no lower than Excellent or Very Good when shopping for a Round Brilliant diamond.
A Round Brilliant’s faceting pattern will hide a small amounts of body color when face up, but we still recommend choosing a diamond above a I color grade to insure a near colorless stone. When selecting a clarity grade for a Round Brilliant we recommend anything in the VS1 to SI2 range. A stone graded above an SI1 should be eye clean. Clear diamonds can be found in the SI1 and SI2 range, but it is best to evaluate them in person to determine if their characteristics are distracting or unnoticeable.
Knox Jewelers is here to help you create a one-of-a-kind custom engagement ring. If you are considering a Round Brilliant center stone, our design consultants can walk you through all of your options and help you choose your perfect diamond. Contact us today to get started on your custom design.