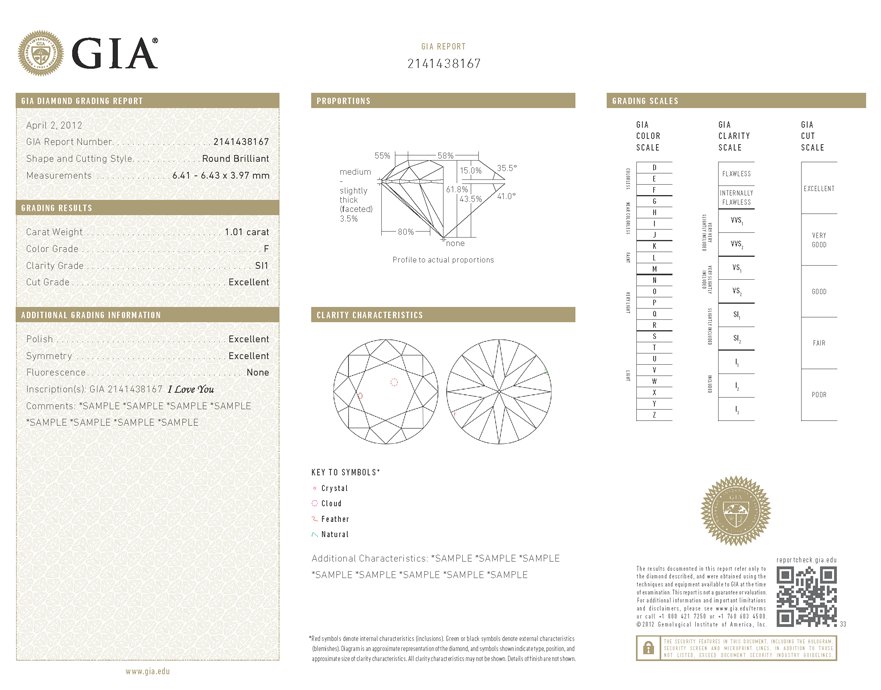
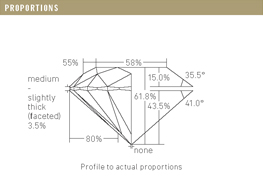
When carbon is exposed to extreme amounts of heat and pressure deep within the earth, the end result is the creation of a natural diamond. This strenuous process can leave a variety of characteristics upon a diamond crystal. Those features enclosed within the gemstone are referred to as inclusions and those left on the exterior are called blemishes. The Clarity Grade of a given diamond, one of the 4Cs, is determined by the presence or absence of these features.
Inclusions, or internal characteristics, will appear during the diamond’s formation. Inclusions will be unique for every single gemstones, essentially giving your diamond a fingerprint that allows you to recognize it apart from all others. There is a variety of inclusions, but the most common types we come across are clouds, feathers or mineral crystals enclosed within a gemstone.
Blemishes are characteristics confined to the exterior of a diamond. Blemishes can occur naturally, or be man-made resulting from the cutting process a faceted gemstone endures.
The severity of a stone’s inclusions and blemishes with determine its clarity grade. The number, size, relief, nature, and position of characteristics are taken into consideration when formulating a diamond’s clarity as it is recorded on its certification. No diamond will be perfectly pure, each gemstone will have some residue from its creations. However, the closer a diamond is to pure, the more rare and valuable it will become.
The GIA Diamond Clarity Scale has six categories, divided into a total of eleven specific grades.
- Flawless (FL) – No inclusions and no blemished viable under 10x magnification.
- Internally Flawless (IF) – No inclusions viable under 10x magnification.
- Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2) – Inclusions so slight they are difficult for skilled grader to see under 10x magnification.
- Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2) – Inclusions are observed with effort under 10x magnification, but can be characterized as minor.
- Slightly Included (SI1 and SI2) – Inclusions are noticeable under 10x magnification.
- Included (I1, I2, and I3) – Inclusions are obvious under 10x magnification which may affect transparency and brilliant.
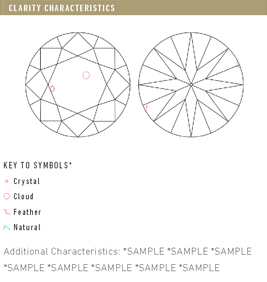
Married to a Clarity Grade on a diamond grading report is a Plotting Diagram. This diagram displays important diamond characteristic information that was seen during the grading process. It is essential a map that tells a deeper story about your center stone. All of a diamond’s important inclusions and blemishes are documented and plotted. Since no two diamonds will have exactly the same diagram, this map will be important in identifying your gemstone if ever need be.
The plotting diagram will roughly resemble the shape and faceting pattern of your diamond. This helps you to understand where the marked characteristics are located on your gemstone. There will be two views shows of the diamond. Its crown view, or top, and pavilion view, or bottom.
In a plotting diagram, a certain color will correspond to each category of clarity characteristics. The colors and symbols used will help you understand the nature of each feature.
- Red – Inclusions
- Red and Green Combined – Inclusions that reach the surface of the diamond like; cavities, indented naturals, knots or laser drill holes.
- Green – Natural Blemishes
- Black – Extra Facets
The diagram below lists common characteristics as they would appear on a GIA plotting diagram. When characteristics are listed on a cert they will appear in order of importance to the clarity grade. If a large, centrally located feather is present in your stone, with few other impediments, it will be seen first in the list of inclusions. This feather most likely determined the final clarity grade of your diamond.

Some clarity characteristics in a diamond may not be plotted on their certification if they are faint or are not important in determining the clarity grade of a gemstone. Featured that are not diagrammed will often be listed in the Comments section of the certification.
A GIA Plotting Diagram is an important tool in understanding the one-of-a-kind characteristics present in your perfect diamond. Keep in mind, that many characteristics are too small to be seen by anyone apart from a trained diamond grader. To your naked eye, two diamonds may look similar even though they drastically differ in grades. What is important is to choose a center stone that speaks to you with the quality standards you desire.
Here at Knox Jewelers, we want to assist you in finding your perfect center stone to feature in one of our custom created settings. You may not desire that gemstone to be a diamond, but if you do, we will walk you through the important features present in the diamond you choose. Contact us today to start the hunt for your perfect diamond, no matter the shape, size or color.